The Role of Mobile Money in Expanding Merchant Acquiring in Africa | By Banji Kayode

2023 marked a profound year in mobile money merchant acquisition in Africa. Why?
This particular year witnessed a skyrocketing increase in the sector of 14%, reaching approximately $74 billion.
This rapid growth shows how mobile money is changing the way businesses accept payments across Africa.
Simply put, mobile money allows people to send, receive, and store money using their phones — without visiting a physical bank. Conversely, merchant acquisition enables businesses to accept digital payments and use other financial technology services often sponsored by a financial institution.
Today, many businesses in Africa no longer struggle with complicated money transactions. In other words, mobile money provides a cheaper, easier, and more convenient way to send and receive cash.
This shift is not only making transfers simpler but also supporting economic growth and driving digital progress across the continent.
This article explores how mobile money reshapes merchant acquisition in Africa. We’ll also examine its evolution, a few case studies, its current landscape, transformative impact, regulatory considerations, and future trends.
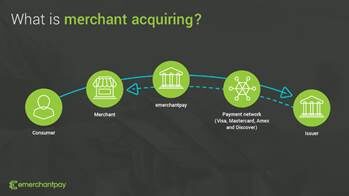
IMAGE: Source: Google
We’ll begin with the foremost
- The Evolution of Mobile Money
Mobile money did not take off overnight. It took years of critical thinking, innovation, government policies, and consumer trust to get to where it is today.
What began as a simple way to send and receive money has now become a saving grace for businesses.
Mobile money is no longer just about personal transactions—it is transforming commerce and financial inclusion.
As asserted by Global Money Dataset and UNCDF Analysis (GSMA), mobile money services have nearly doubled in a decade, increasing from 169 services in 71 countries (2012) to 316 services in 98 countries (2021). This expansion has given millions of unbanked people access to financial services.
Even more striking is the surge in registered users, which jumped from 134 million to 1.35 billion with a total transaction of over $1 trillion in just 10 years.
As more fintech solutions continue to advance, mobile money will keep closing financial gaps, supporting businesses and individuals, and boosting economic development.
A future analysis by Ericsson states that progress in these areas will shape the world of digital finance, making transactions quicker, more secure, and widely accessible.
Also, with ongoing technological advancements, mobile money will keep closing financial gaps, supporting businesses and individuals, and boosting economic development.
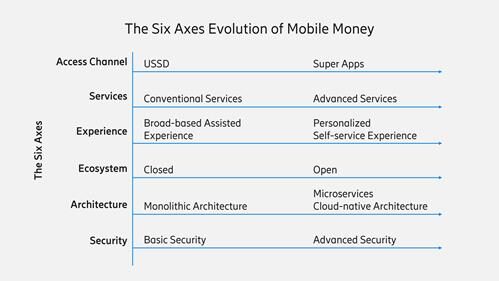
IMAGE Source: Google
- Notable Case Studies
Since its inception in March 2007, the famous Kenyan M-PESA Recorded a significant milestone in this journey. Originally designed for peer-to-peer transfers, it gradually expanded into an all-encompassing financial ecosystem.
Other telecom providers in this line include MTN MoMo in countries such as Tanzania, Nigeria, and Uganda, as well as Francophone Orange Money. These fintech pioneers have demonstrated that mobile money transactions can facilitate transparent and more secure business operations.
Africa’s high mobile penetration has been instrumental in this transformation. As of January 2023, South Africa alone had approximately 112.7 million mobile connections, highlighting the widespread reach of mobile technology.
This extensive connectivity made mobile money a practical solution for delivering financial services, especially in regions with limited traditional institutions.
In addition, mobile money merchant acquisition has also had its fair side of challenges, some of which still prevail. But despite these hurdles, mobile money continues to evolve. It is no longer just a transfer service but a pivotal aspect of business growth. Nonetheless, one of the ways to sustain its prevalence is to make it even more accessible and cost-effective for merchants across Africa.
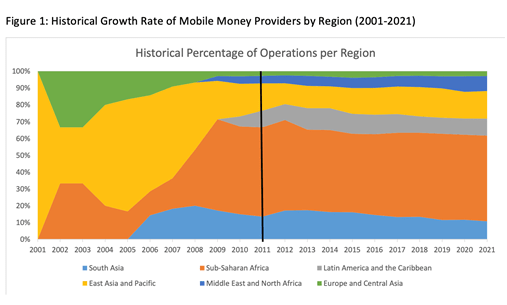
IMAGE Source: GSMA (Global Money Dataset and UNCDF Analysis)
Before we discuss how mobile money is transforming the merchant landscape in Africa, let’s look at how the industry is fairing at the moment.
- The Merchant Acquiring Landscape in Africa
For years, merchant acquisition in Africa has been dominated by traditional banking systems. However, these systems have struggled to serve the continent’s diverse and largely informal economy. Some of its major challenges include:
- High setup costs: Though often referred to as the backbone of the economy, some small and medium-scale businesses still cannot afford expensive Point-of-Sale(POS) terminals and transaction fees. This deficiency may cause such enterprises to return to the traditional (stressful) business model.
- Limited network reach: While urban areas appear to be the benefactors of emerging banking infrastructure, urban locales are left in the dark to grapple with poor network coverage, leaving rural merchants without access to digital payment solutions.
- Slow settlement times: Since traditional systems involve lengthy processing times, payments can be delayed, making businesses that rely on daily cash flow go through the pain of surviving for the day,
Extensively, due to these challenges, over 90% of retail transactions in Africa still rely on cash.
Thankfully, mobile money is changing the story by providing affordable, easy-to-use, and scalable solutions that help businesses of all sizes thrive.
Here is where it becomes more exciting…
How Mobile Money is Transforming Merchant Acquisition in Africa
We’ve already established that mobile is a lifesaver. Here are key areas in which it aims to solve some of the prevailing challenges in African merchandise.
Mobile money eliminates the barrier of getting traditional Point-of-Sale (POS) systems. Acquiring a POS often requires physical terminals, bank partnerships, and high transaction fees (2–5%). For small businesses, these costs make digital payments quite unaffordable. Mobile money ensures merchants no longer need costly hardware to run their business transactions. All they need is a mobile phone and a registered bank account to cash in and out on daily transactions. The most interesting side of this is that these transaction fees are significantly lower, often below 2%, making digital payments accessible even for micro-businesses. This transition is not just about cost savings but also about increasing sales. As more people embrace cashless payments, merchants who accept mobile money attract more customers and boost revenue.
Interoperability and digital wallets are other ways mobile money is fixing one of Africa’s biggest financial challenges. This problem often happens because different payment platforms don’t connect well. That’s why fintech companies like Flutterwave, Paga, and OPay help link banks and digital wallets. Now, businesses can receive money with little or zero charges.
In the same way, QR codes and USSD transfers are making transactions easier, especially in areas with little or no internet. Even small traders can send and receive payments on basic feature phones. All they have to do is follow the directions programmed on the platform. Today, African merchants can boast of a 40% increase in mobile money transactions ? a brilliant shift from conventional cash operations.
E-commerce and social commerce integration is another breakthrough for merchant acquisition. Social media platforms like WhatsApp, Instagram, and Facebook Marketplace are top team players in terms of mobile money. Beyond brand offering brand visibility, these platforms eliminate physical transactions, enabling instant, hassle-free payments. For example, digital payment solutions like JumiaPay, KongaPay, and Paystack make online checkouts smoother for African businesses.
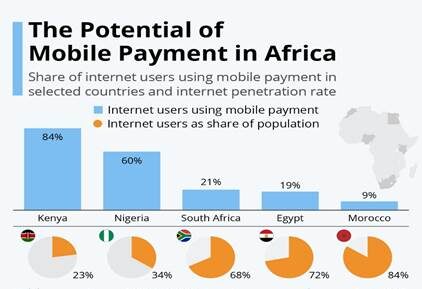
IMAGE Source: Statista
In summary, mobile money has made payments easier, faster, and more affordable for everyone—from small shop owners and market traders to big companies. It has opened new doors for millions of entrepreneurs, giving them a secure and hassle-free way to run their businesses and grow.
However, looking ahead, mobile money will keep improving. Transactions will become even quicker and more secure, and businesses will connect more easily with global markets, opening up new opportunities beyond their local communities. Governments are also pushing for digital payments, making financial services more accessible to everyone.
As more people get smartphones and internet access expands, mobile money will blend seamlessly with online shopping, social media, and digital banking. Smart financial tools powered by AI will help businesses track their money, get loans, and even save for the future. In the long run, mobile money is about more than just sending and receiving payments — it’s about giving businesses the freedom to grow and shaping Africa’s economy for years to come.
About the Author
Banji A. Kayode is a fintech expert specializing in merchant acquiring and payment system infrastructure for banks and major operators. With deep experience in digital payments, he has been instrumental in driving financial inclusion and innovation within the fintech sector. A recognized thought leader, Banji frequently shares insights on emerging digital financial services and cutting-edge payment technologies. Beyond his industry contributions, he serves as a trusted advisor to fintech startups, offering strategic guidance on product development, market entry, and regulatory compliance.







Thank you for reading
💯
Good
I love your creativity!
Good one sir
nice one baba👍