Building Effective Tech Mentorship Programs: Bridging the Skills Gap in Nigeria Markets

How structured mentorship can bridge Nigeria’s 720,000-person skills gap and accelerate career growth in the tech ecosystem
In the bustling tech hubs of Victoria Island and Yaba, a quiet crisis is unfolding. Despite Nigeria’s emergence as Africa’s startup capital, with over $1.37 billion in tech investments flowing into the country in 2023, a massive talent shortage threatens to undermine this remarkable progress.
The numbers tell a sobering story: Nigeria faces a skills gap of 720,000 tech professionals as of August 2023. Yet paradoxically, unemployment among young graduates remains high, with many lacking the practical skills demanded by the rapidly evolving digital economy.
The solution, according to industry leaders and successful case studies, lies not in traditional education reforms alone, but in structured mentorship programs that can bridge the chasm between academic learning and industry requirements.
Key Insights
Key Finding: Tech professionals with mentorship support advance 40% faster in their careers compared to those relying solely on self-directed learning.
The Magnitude of Nigeria’s Skills Crisis
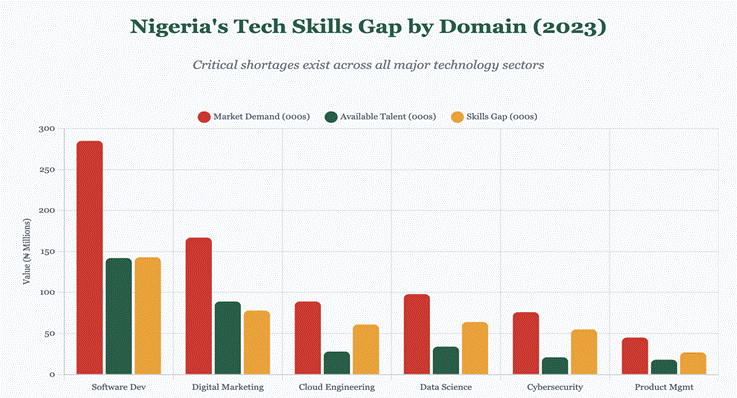
Nigeria’s technology skills shortage represents approximately 65% of total demand, making it one of the most severe skills gaps globally. In software development alone, market demand has reached 285,000 positions, but only 142,000 developers are available – a 143,000-person deficit worth approximately ?600 billion annually in unfilled economic potential.
Understanding Nigeria’s tech talent landscape in August 2023

The situation becomes critical in specialized fields. Data science shows 98,000 positions demanded but only 34,000 qualified professionals available. Cybersecurity faces a 55,000-person gap (76,000 needed, 21,000 available), representing a critical vulnerability to Nigeria’s digital infrastructure. Cloud engineering shows 89,000 demand with only 28,000 available, constraining modernization efforts across enterprises.
Conservative estimates suggest unfilled positions represent 2.4 trillion in lost economic output annually, equivalent to 1.2% of Nigeria’s GDP. This encompasses direct economic value and multiplier effects of reduced innovation and delayed digital transformation.

The Mentorship Void: Current State Analysis
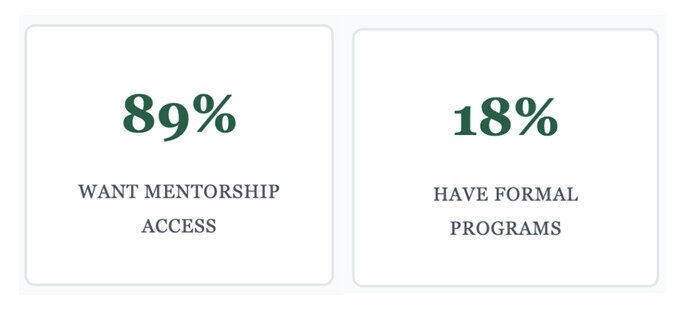
The 2023 Nigeria Tech Professional Survey of 2,847 respondents reveals a stark disconnect between desired and available mentorship support. Only 12% of entry-level professionals have formal mentorship access, despite representing the largest workforce segment with greatest potential benefit. Mid-level professionals fare slightly better at 23%, while senior professionals report 31% access.
Without structured mentorship, 67% rely primarily on YouTube tutorials and self-directed learning, 23% use peer networks, and only 12% access bootcamps. While valuable, these cannot replicate personalized guidance, real-world context, and professional networking that effective mentorship provides.
Professionals with mentorship support advance 40% faster, earn 28% higher salaries within three years, and report 65% higher job satisfaction. Time constraints (43%), lack of structured frameworks (38%), and geographic limitations (29%) represent primary barriers to mentorship program development.
Proven Success Models
1. Andela: Comprehensive Developer Training Excellence
Andela’s six-month intensive program combines technical training with comprehensive mentorship, achieving remarkable results: 3,000+ developers trained since 2014, 94% job placement rate, 340% average salary increase, and 89% still in tech careers after five years. The model pairs participants with experienced mentors who commit 8+ hours weekly to technical guidance and career development.
2. Flutterwave: Internal Peer-to-Peer Mentorship
Flutterwave’s model pairs senior engineers with junior colleagues, delivering 78% faster onboarding (3.2 weeks vs. 14.6 weeks), 45% code quality improvement, 89% employee satisfaction, and 94% retention rates. The program emphasizes collaborative learning and cross-functional knowledge sharing.
3. Techstars Lagos: Global Mentorship Networks
Each startup works with 8-12 mentors during the three-month program, achieving 120+ startups mentored, $180M+ in follow-on funding, and 85% three-year survival rate. The model demonstrates how global expertise can be adapted to local contexts while providing world-class guidance.
The IMPACT Framework for Mentorship Excellence
A systematic methodology for designing, implementing, and scaling effective mentorship programs, developed through analysis of 50+ initiatives across the African technology ecosystem.
1: Identify
Comprehensive needs assessment and gap analysis through surveys, interviews, and market research to understand specific skill gaps and career development requirements.
2: Match
Strategic mentor-mentee pairing based on technical skills, personality compatibility, communication styles, and career aspirations using systematic assessment tools.
3: Plan
Structured learning pathways with clear milestones, customizable goals, and diverse learning modalities from hands-on projects to industry exposure.
4: Act
Implementation excellence through regular engagement, consistent communication protocols, and robust support systems for sustained mentorship relationships.
5: Check
Continuous assessment and optimization through multiple feedback mechanisms, progress tracking, and program adjustments based on outcomes.
6: Transition
Career advancement support and alumni network development, creating sustainable communities that provide ongoing value and mentorship opportunities.
The Mentorship Economy Opportunity
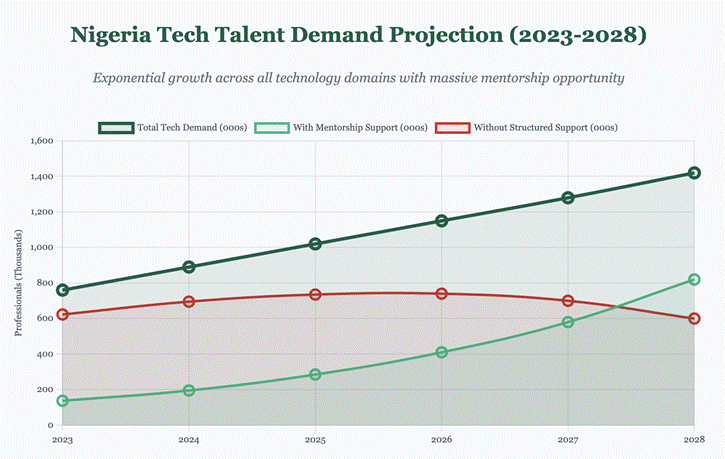
By 2028, the mentorship gap could reach 880,000 professionals without structured support. Organizations that can bridge this gap will capture significant economic value while positioning Nigeria as a talent development hub for the broader African technology ecosystem. This represents not just a business opportunity, but a chance to establish Nigerian expertise in talent development as a competitive advantage in regional markets.
Strategic Recommendations for Action
A: Government & Policy
- Establish National Tech Mentorship Initiative with ?50B five-year funding
- Create tax incentives for companies investing in mentorship programs
- Integrate mentorship into NYSC program for tech graduates
- Partner with telcos for digital infrastructure supporting remote mentorship
- Develop regulatory frameworks for mentorship program quality standards
B: Private Sector
- Allocate 2-3% of senior staff time to formal mentorship activities
- Establish industry consortiums for shared mentorship resources
- Integrate mentorship into talent acquisition and retention strategies
- Create clear career progression pathways incorporating mentorship milestones
- Leverage international expertise for global perspective mentorship
C: Educational Institutions
- Establish comprehensive industry partnership programs with mentorship integration
- Train faculty in modern mentorship methodologies and industry practices
- Incorporate real-world projects pairing students with industry mentors
- Develop systematic alumni networks for ongoing mentorship opportunities
- Create industry advisory boards for curriculum and mentorship guidance
D: Tech Professionals
- Commit 2-4 hours weekly to mentoring junior colleagues consistently
- Pursue formal training in mentorship techniques and career counseling
- Build diverse professional networks for broad mentorship opportunities
- Share knowledge through writing, speaking, and content creation
- Actively participate in mentorship platforms and community building
The Time for Action is Now
Nigeria stands at a pivotal moment in its technological evolution. The country’s emergence as Africa’s technology leader is remarkable, but sustaining this position requires immediate action to address the skills gap through effective mentorship programs.
The evidence is overwhelming: 720,000 unfilled positions, 89% seeking mentorship, and proven success models demonstrating 40% faster career advancement and 80%+ job placement rates. The opportunity for transformative impact is extraordinary, but it requires coordinated effort across all ecosystem stakeholders.
The economic stakes are massive – ?2.4 trillion in potential value and 1.2 million professionals needing development by 2028. But more importantly, this is about unlocking Nigeria’s greatest asset: its remarkable human capital.
“The future of Nigeria’s technology ecosystem depends not on the talent we have, but on the talent we develop. Mentorship is the bridge that will carry us across the skills gap to sustained technological leadership.”
___________________________________
Written by: Emmanuel Efosa Agho , Software Engineer & Tech Evangelist







