Blockchain Will Redefine Company of the Future – Digital Encode CTO

Dr. Oluseyi Akindehinde, the Co-founder and Chief Technical Officer (CTO) of Digital Encode Limited, has identified blockchain and the mobile phone as going to be fundamental to the company of the future.
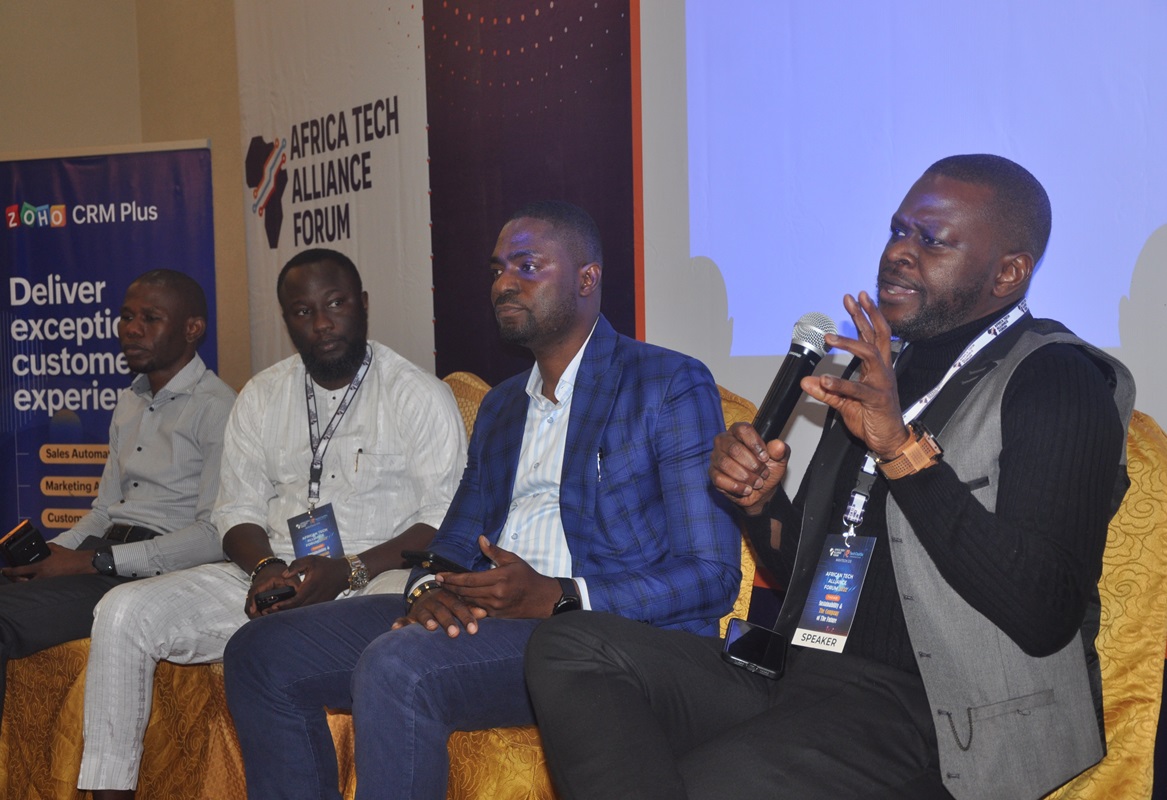
Making a presentation at the just concluded Africa Tech Alliance Forum, otherwise known as AfriTECH 2.0, held in Lagos, recently, Akindehinde said that with the coming of the 5G technology, it is expected that the company of the future has to provide services along those lines.
The cybersecurity expert however, argued that it is doubtful that humans will completely live their lives using such tools as the mobile phone and the internet without any other thing explaining why he titled the presentation “Web 3.0, Blockchain and a decentralized digital identity.”
According to Akindehinde, “Blockchain is actually three things. Blockchain is a protocol, like when you have an email, for instance. Email has an organized protocol; it is called SMTP. Blockchain is also a protocol.
“Number two, why do you have a protocol? It presupposes that there is a network; there are servers that host the email. The last thing about blockchain is that it is software. That means you have the SMTP, the servers, and the software.
“When we talk about blockchain in this part of the world, it is usually an anonymous cryptocurrency. Cryptocurrency is just the work of four quadrants which are fungible, non-fungible, transferable, and non-transferable.
“Cryptocurrency is fungible and transferable. When we talk about it being fungible, if I bring out a thousand naira note, for instance, you can bring yours, and we exchange it; it doesn’t matter. The problem with a physical asset like that is that we can only make that transaction when we are in the same space,” he further disclosed.
While explaining the difference between electronic transaction and digital transaction, Akindehinde stated that what people often do online is electronic because there is somebody in the middle granting access.
“When you log onto your bank mobile app and you make a transaction from bank A to bank B, what you are doing is transferring messages; it’s like email. When you take your ATM card to an ATM, what you are doing is that you are delegating control of that transfer to that man in the middle which is your bank.
“This brings out two things: The concept of ownership and the concept of control. So, when you are doing that electronic transaction, you do not own that transaction, you are only in control of it. If the network goes down, you can no longer do that transaction.

“Your university degree for instance, is an asset to you, it’s unique to you; it’s non-transferrable. Unlike money you can exchange with another person, you cannot exchange your certificate with another person.
“Why can’t we, therefore, have a digital driver’s license or a digital passport, or a digital identity management system? Why are we still carrying plastics? That is why there is the need to power a digital economy through decentralized identities.
“We all have BVNs and NINs, why can’t I be authenticated with my NIN for instance, and I sign in and go? When you are online and you go and authenticate to your bank, by putting your username and password, your bank is not authenticating to you,” he said.
On the difference between Web 2 and Web 3, the Digital Encode CTO said that “Web 2 simply means that something is entirely online. I can’t use what is online in the physical world. For instance, if you have Gmail, Google Authentication or Microsoft, you can only use it on Google. The authentication resides on the server of the bank. That is the entire concept of Web 2.

“Web 3.0 on the other hand simply means that instead of having all the things stored on a centralized internet, you now have the data in your control; you are the owner, and you are in control of it. And that is why we have what is called a self-solving identity system.”
Dr. Akindeinde also received “AfriTECH Blockchain Technology Mastery Personality Award 2022”.